Cathodic protection of the vessel with sacrificial anodes
Vessel corrosion – cathodic protection and sacrificial anodes
To achieve cathodic protection of the vessel with a sacrificial anode system, certain tools and techniques must be used. Vessels are among the structures that are most exposed to corrosion due to the environment in which they operate. Seawater is a very corrosive environment because the salt in it makes it a very good conductor of electricity and leads to the oxidation of iron by releasing many ions. Almost every part of the vessel is subject to corrosion of varying severity.
Parts of the vessel that are underwater or exposed to water, some of which are:
Exterior hull, rudder, impeller shaft, ballast tanks, ballast pipes
There are several ways to protect the hull and other parts of the vessel from corrosion. The method chosen depends on the area to be protected, its shape and environment. There are three major ways to protect against corrosion:
- Coating with anti-corrosion paints
- Cathodic protection system of sacrificial anodes
- Impressed current system
In this article, we will discuss the method of cathodic protection system of sacrificial anodes.
Classification of anodes
Anodes can be classified according to their shape, size, type of raw materials and method of installation at the protected level. Anodes can be used in small or large sizes, and this affects their weight and the overall weight of the protected structure. The size and shape of the area to be protected, availability and access to space, and structural strength considerations are factors that affect the size and weight of the anode.
Anode shape
Anodes can take many forms depending on their application. Sacrifice anodes are produced in various forms such as flat or block shaped, cylindrical or semi-cylindrical, tear anodes, bracelet anodes, disc anodes and tubular anodes.
The choice of anode shape depends on several factors. Some of these factors are:
- Shape of the protected surface,
- Availability of sufficient space to install the anode,
- Availability
- Easy installation.
For example, flat anodes are mostly used for large, flat surfaces such as the hull. In high-speed boats, where flowing water is very important, tear anodes are used because flat anodes increase the boat’s strength. Bracelet anodes are used for pipelines and impeller tentacles, while tubular anodes are used for cables. Of course, in some cases the choice depends on the availability, cost and flexibility in the design. For example, if the cost is high, cylindrical anodes can be used to protect pipelines instead of bracelets.
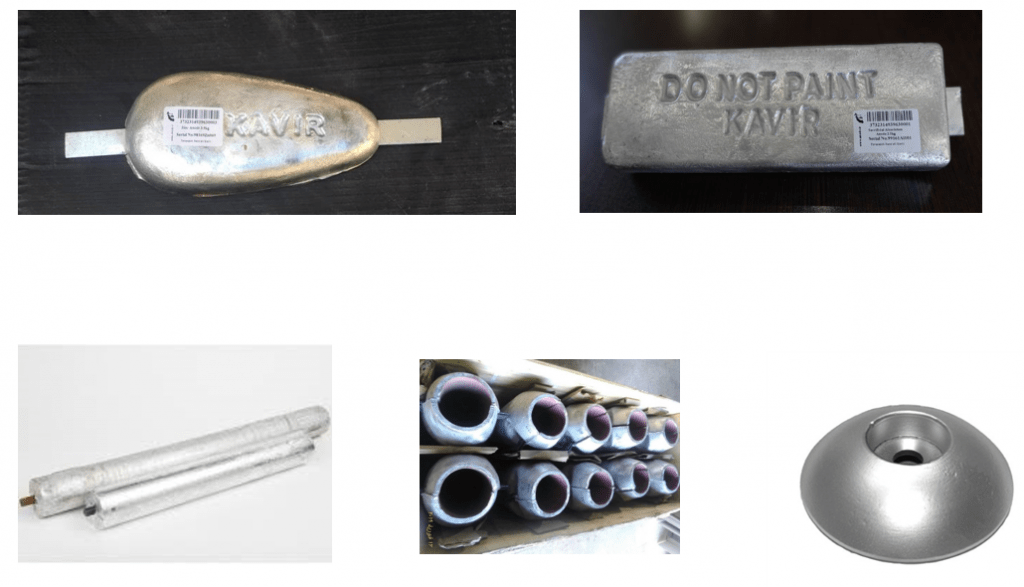

Anode type
Zinc or aluminum sacrificial anodes are commonly used for marine applications. Two features of anode performance measurement are listed below.
- Closed circuit potential indicates ease of anode corrosion. The more negative the value, the corrosion is easier.
- Electrochemical capacity (Amp-hr / kg) indicates the amount of anode material consumed.
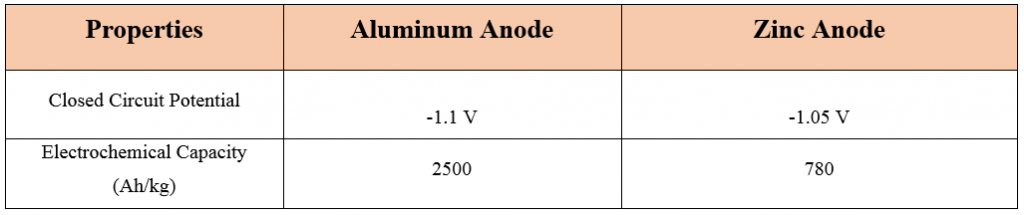
From the table above it can be seen that aluminum has a higher closed circuit potential, so it starts working faster than zinc. It also has a higher electrochemical capacity than zinc and will last longer at the same weight.
In addition, zinc anodes in freshwater tend to form a calcareous coating on the anode surface that prevents them from working effectively. However, zinc anodes are sometimes more reliable in low-oxygen environments, such as marine sediments or areas with high bacterial activity. Therefore, while aluminum is more efficient, the use of zinc may be more effective in some cases.
Aluminum anodes can also ignite if they fall from a height on oxidized steel. Therefore, their use inside cargo tanks is not recommended. Therefore, the choice of materials depends on the type of environment in which the anode is placed and must be done carefully.
Anode installation methods
There are three basic ways to install an anode on a protected structure:
- Welded connection
- Connection by bolts
- Gutter connection
Welded connection ensures the closest and safest contact between the anode and the body, and electrical conduction through the insert is well done. But sometimes welding is not possible due to lack of access or favorable conditions. Therefore, the connection can be used with bolts or studs. In addition, it is easier to replace anodes connected with bolts than to weld.

Tavana Zob Sana’ati Kavir Company, in the field of cathodic protection of vessels with sacrificial anodes and similar tools, is able to produce sacrificial aluminum and zinc anodes in different dimensions and shapes according to the client’s request. You can contact the sales department for more information.
- Published in Articles, Educational, Scientific
Applications of sacrificial anode systems
The method of sacrificial anodes and its applications
In the sacrificial anode method, the current required to combat the corrosion of the structure is provided by another metal, which is usually made of zinc, aluminum and magnesium. Because these sacrificial anodes do not have the ability to provide high current, sacrificial anodes are used where low current is required to protect against corrosion.
Applications of sacrificial anodes include the following:
- Where the protected structure is small.
- Items that do not have access to electricity, such as offshore platforms or pipelines.
- Items where the use of electricity is dangerous, such as inside oil storage tanks.
- Where soil specificity is low. The use of sacrificial anodes in high-strength soils is not recommended due to reduced output current.
- To fix the wandering currents.
According to the above, you can get the necessary information about cathodic protection from the sales and development unit of Tavanazob Sana’ati Kavir Company regarding the applications of the sacrificial anode system, and follow other questions about the applications of the sacrificial anode system from the sales support department.
In this regard, you can receive the contact numbers of the sales and development unit from the relevant department or send questions related to cathodic protection or sacrificial anodes via e-mail.
- Published in Articles, Educational, Scientific
Cathodic protection of aboveground storage tanks
Protection of aboveground storage tanks against corrosion
Both sacrificial anodes and impressed current system are used for cathodic protection of aboveground storage tanks. In this method, the protection of the inner surface of the tank is done by the method of sacrificial anodes and the protection of the outer surface of the tank floor is done by ribbon MMO anodes. Because the tank has large dimensions and therefore high weight, to support the weight of the tank, ribbon anodes with a flat cross section are used. Also, flat anode will lead to better flow in the tank floor. Before placing the bottom and body of the tank in the desired location, first the anodes are installed in the correct way, then a special layer of sand is poured on it and finally the bottom of the tank is placed on the sand.
Cathodic protection of the tank floor
The impressed current cathodic protection system is placed in the bottom of the tank in such a way that first the ribbon MMO anodes are laid in the form of horizontal strips in the bottom of the tank and in order to connect the anodes to the rectifier, the conductor bar which are titanium strips without cover, are used perpendicular to ribbon anodes. The connection of titanium bar to ribbon anodes is done by spot welding. The negative phase of the rectifier is connected to several points of the tank body. The positive phase of the rectifier is connected to a junction box and then through it, titanium bars is attached to the anode. The job of titanium is to deliver current to the anode. These connections are well done in different places so that no interruptions occur. Also, a number of permanent reference electrodes are placed on the bottom of the tank so that the potential of different parts of the tank can be measured.
![]()
In the past, other methods were used to cathodically protect the tank around it, such as drilling wells and placing anodes around the tank. But these methods did not bring the flow evenly to the bottom of the tank.
Cathodic protection inside the tank
The ribbon anodes inside the soil only protect the outer surface of the tank floor from corrosion. Because there is a different electrolyte inside the tank, such as water or crude oil, other anodes must be used to protect the inside of the tank. Sacrificial anodes, and in some cases impressed current anodes, are commonly used to protect the inner surface of the tank. Inside the crude oil tanks, only the sacrificial zinc anode is used.
- Published in Articles, Educational, Scientific
Types of backfill in cathodic protection system
Types of backfill
The type of backfill used in the cathodic protection system in ground substrates depends on the type of cathodic protection system used. Due to the fact that the cathodic protection system exists in two types of sacrificial anode systems and impressed current anode systems, so two types of backfill materials are also used.
Sacrificial anode systems
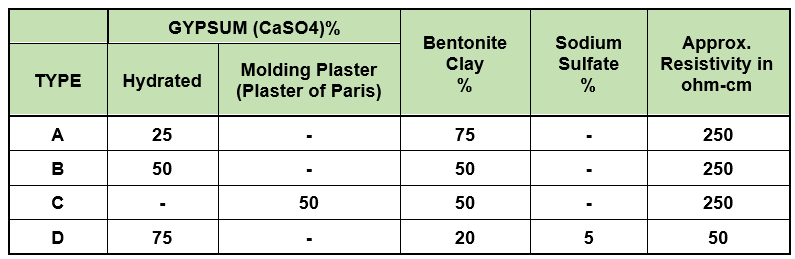
The sacrificial zinc and magnesium anodes used to cathodic protection of structures buried in the soil are sometimes packed in a linen bag with a backing material. These materials reduce the local corrosion of the anode by preventing the anode from coming into direct contact with the soil. It also prevents the anode from becoming passive by reacting with salts in the soil. The backfill used improves the performance of the anode by creating a low-resistance environment around the anode. These materials are generally a combination of three types of gypsum gypsum, bentonite and sodium sulfate, and the percentage of their compounds depends on the environment used.
The following table shows the types of backfills according to the IPS-M-TP 750 standard:
Impressed current system
Impressed current anodes for cathodic protection of underground structures are usually surrounded by a carbon backfill. The purpose of using this support is:
- By reducing the resistance of the environment around the anode, it leads to an increase in the amount of current produced by the anode.
- As the anode level increases, the amount of current increases.
- Reduce anode consumption rate and thus increase anode lifetime.
Carbon backfill according to IPS-M-TP 750 standard is available in three types of 80% metallurgical coke, 90% petroleum coke and 95% special petroleum coke.
The chemical composition of these three types of backfill is specified in the table below:
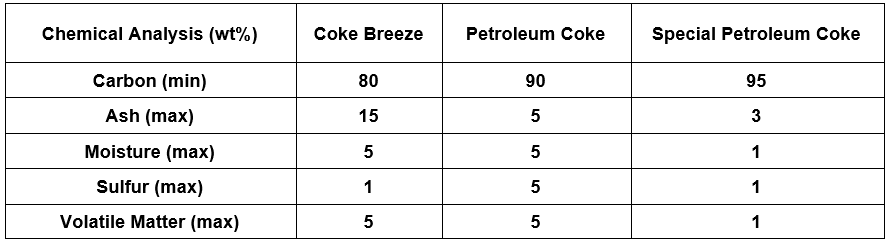
Coal coke is generally used in shallow horizontal substrates. Petroleum coke or special petroleum is used for deep wells.
- Published in Articles, Educational, Scientific
Mixed metal oxide anode (MMO) and its applications
What is a mixed metal oxide anode?
Mixed metal oxide anodes are made of a titanium substrate coated with mixed metal oxides. The coating is applied by several thermal processes on the titanium base to create a chemical resistant layer. Due to the inherent stability of titanium, this coating achieves the best performance of the anode by strengthening the conductivity of the anode.
MMO anodes have advantages such as very low consumption rate and high current capacity. Low anode consumption rate causes the anode dimensions to remain almost constant over the life of the anode. Therefore, these anodes are widely used in impressed current systems for land and marine structures.
MMO anode applications
MMO anode is used in cathodic protection system in different types of tubes, ribbons, meshes, wires and plates. These anodes can be used effectively in all environments such as soil, fresh water and saline water. Depending on the environment in which the anode is located, two types of coatings are considered for the anode. Iridium-tantalum coating is used in soil and fresh water and iridium-tantalium-ruthenium coating is used in saline water. The anode current capacity in soil, coke or fresh water is 100Amps \ m2 and in saline water is 600Amps \ m2.
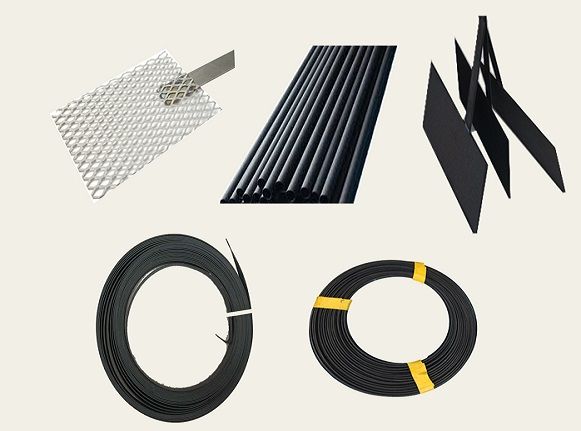

various type of MMO anodes
Types of MMO anodes
- Tubular Anode
Tubular anode is the most common type of MMO anode used in cathodic protection systems. The titanium of this anode is manufactured according to ASTM B338 Grade1 standard. Tubular anodes are usually used as strings in deep wells.
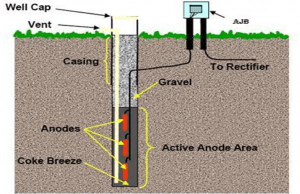
cathodic protection of deep wells by tubular mmo anodes
- Ribbon Anode
The titanium base of these anodes is manufactured according to ASTM B265 Grade1 standard and uses iridium / tantalum mixed metal oxide coating. This type of anode is used to protect the external bases of aboveground storage tanks. Ribbon anodes are suitable for connection to titanium conductors by spot welding to create a network under the tank that also provides a uniform distribution of current.
- Mesh Anode
Mesh MMO anodes are used in cathodic protection systems of reinforced concrete structures. Titanium mesh anode base like ribbon anode is produced according to ASTM B265 Grade1 standard and the anode quality is checked according to NACE TM0294 standard.

- Wire Anode
Titanium wire anode is an ideal cathodic protection product for protecting the bottom of tanks, submarines and pipelines. This type of anode is made of high grade titanium with a mixed metal oxide coating and has a lifetime of more than 50 years.
- Plate Anode
These types of anodes are designed as rectangular or circular plates for use on ships and vessels.
- Published in Articles, Educational, Scientific
Protection of water heater against corrosion
Maintenance of water heaters using a sacrificial anode
The use of water heaters in industry as well as in homes in various dimensions and shapes is essential. Therefore, its maintenance is very important. The water heater may run loudly over time as sediment builds up inside. This deposit may be due to natural minerals in the water or substances that result from corrosion of the sacrificial anode or the tank itself.
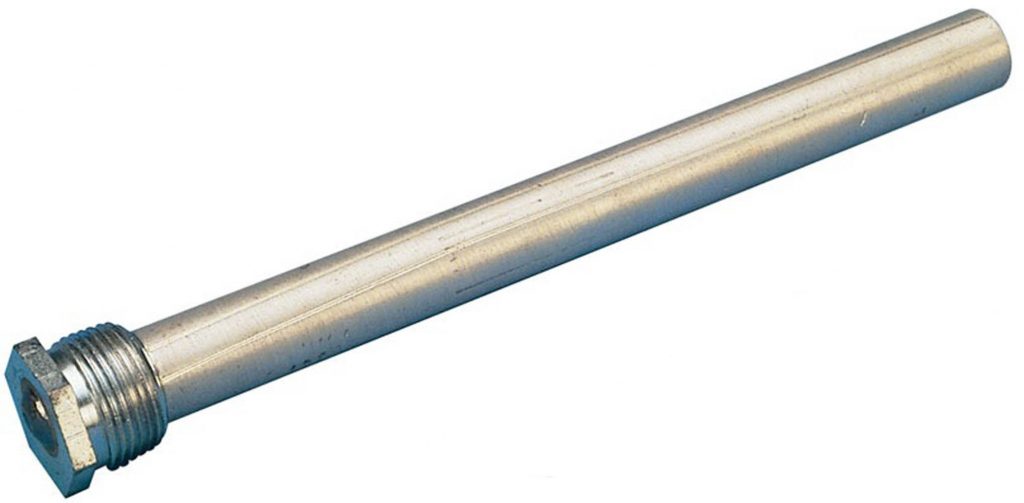
In a water heater, the sacrificial anode is visible as a rod that slowly erodes over time. The sacrificial anode is made of magnesium, aluminum or a combination of zinc and aluminum. The water in the tank causes corrosion of the inner steel of the tank by creating an electrolytic reaction. To protect the steel, a magnesium or aluminum rod anode is placed in place. After the anode corrodes, the tank steel begins to corrode and the tank fails.
Replacement time of sacrificial tank anodes
To protect the tank steel against corrosion, the sacrificial anode of the tank should be replaced every 3 to 5 years, depending on the type of tank. The warranty period of the tank can be used to determine the time of replacement of the anodes. If the anodes are not replaced in time, the tank will continue to work, but over time, the tank steel will corrode and tank replacement will be inevitable, which will cause a lot of damage.

water heater tank corrosion
How to place the sacrificial anode in the tank
The sacrificial anodes are usually screwed to the top of the tank for easier access. Note that sometimes the length of these bars is long and you have to have enough space to take them out. Therefore, sometimes it is necessary to remove the tank to replace the sacrificial anode.

Water heater anode
What type of sacrificial anode is used in the tank?
The sacrificial anode type is usually recommended by the manufacturer. Aluminum sacrificial anode, although it may cost less, has a higher corrosion rate than magnesium anode. Also, in addition to making noise, the aluminum poured into the tank pollutes the water in the tank. Therefore, be careful never to use hot water from the tank for drinking or cooking. The most common sacrificial anode in water heater tanks is the magnesium sacrificial anode.

- Published in Articles, Educational, Scientific







