Cathodic protection of pipelines
The role of cathodic protection of pipelines in the oil and gas industry
One of the main and very costly problems in large industries such as gas, oil, petrochemical, shipping, etc., is the corrosion of metal structures.
In the oil and gas industry, carbon steel pipelines are used to transport hydrocarbons from jackets to production platforms and storage tanks, and enter refineries through pipelines. Carbon steel pipelines are the safest and least expensive way to transport large volumes of hydrocarbons over long distances.
Fuel and water transmission pipelines and other structures buried in soil or submerged in water, due to their metallurgical conditions, are in a state of corrosion and after a while, the performance of the structure is disrupted.
Corrosion in the oil and gas industry dramatically increases the overhead costs of plumbing operations due to the replacement of worn equipment and damage to adjacent equipment. Therefore, it is necessary to use a proper protection system to prevent corrosion.
Corrosion control mechanism in cathodic protection of pipelines
Corrosion control mechanisms in oil and gas pipelines are mitigation measures to eliminate or reduce corrosion to prevent pipeline failure and related consequences such as crop failure, environmental pollution and potential accidents.
Five control mechanisms to minimize pipeline corrosion and cathodic protection of pipelines that must be considered during the design and construction of pipelines include design, material selection, coating, cathodic protection, and chemical protection.
Designing
One of the important factors in corrosion control is design. Proper design of a steel pipe increases the life of the structure. Gaps, steel geometry, sharp edges, welded joints, and pipeline connections such as flanges, valves, and pipe supports are often subject to local corrosion due to fluid penetration and dissolution.
In addition, these environments have poor coverage due to inaccessibility or sensitivity to coverage failure. These factors contribute to corrosion and should be carefully considered during the design phase to limit corrosion.
Material selection
The choice of materials is very basic in terms of engineering design to reduce corrosion. The choice of material depends on the environmental conditions such as the fluid being transferred, the temperature, the pressure and the electrolyte in which the pipe is placed (water or soil). Also in flange joints, piping and general joints where it is possible to pair metals of different materials, to prevent galvanic corrosion, care must be taken in determining the material.
Due to its good mechanical properties, availability and low cost, carbon steel, despite its low corrosion resistance compared to other corrosion-resistant alloys, is the main material for pipeline transmission.
coating
One of the main and simplest methods of protecting pipelines is coating. A suitable coating prevents direct contact of the outer surface of the tube with the surrounding environment and thus prevents the flow of ions through the electrolyte, thus limiting corrosion.
There are different methods and types of coating and the choice of its type depends on the type of material selected:
- Painting
Painting is used in environments where the equipment is only exposed to air and no electrolyte is available.
- Coating
The main types of coatings for coating structures that are exposed to electrolytes are strong coatings such as polyethylenes, bitumen and polypropylene.
- Lining
Lining the surface of the structure with rubber sheets.
- Cladding
coating one metal with another.
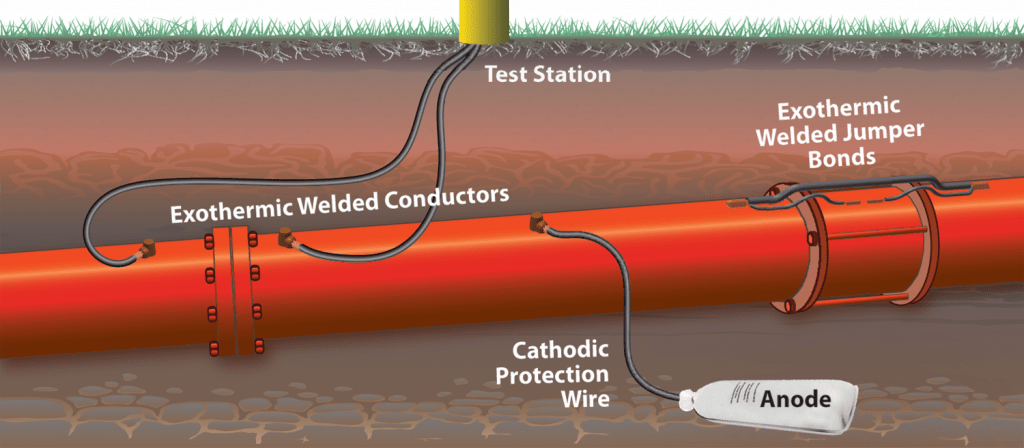
- Cathodic Protection
Using a cathodic protection system along with coating is an effective way to prevent corrosion of pipelines.
There are two general methods for cathodic protection of pipelines:
- Sacrificial anode system
- Impressed current anode system
In cases where the length of the pipeline is very long and in the presence of stray currents, an impressed current system is used to protect the pipeline.
Chemical protection
Chemical protection includes corrosion inhibitors, Oxygen purification system, and biocide in a chemical process.
In the chemical process, biocide is injected into the system, liquid or water to kill microorganisms such as reduced bacteria that increase corrosion under microbiological effects with sulfide. Oxygen scavenging chemicals are injected into the water to deoxygenate to reduce the severity of the corrosion and ultimately achieve adequate cathodic protection of the pipelines.
- Published in Articles, Educational, Scientific


